Are the Poor the Weak Link? Democratic Support and Income Levels in Post-Crisis South Korea
Abstract
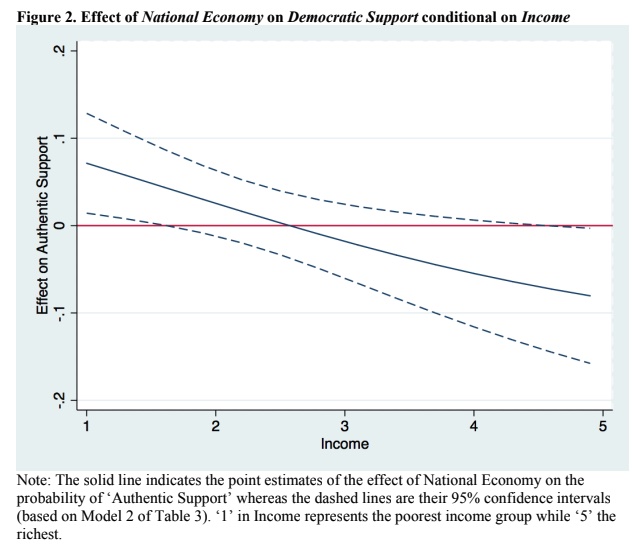
Extant literature on democratization documents that ordinary citizens’ unconditional support for democracy is indispensable to democratic consolidation. Yet observers of nascent democracies have repeatedly witnessed that such support often hinges upon their economic conditions. This paper argues that income levels have a conditioning effect on this relationship; the Korean poor see democracy as a tool for income redistribution and are less likely than the rich to support it when economic hardships appear to close windows of opportunities for such redistribution. Using survey data from the first round of the Asian Barometer Survey on South Korea, I find strong empirical support for this argument. The implication of this finding for broader literature on democratization is that the weakening of young democracies can be attributed to the poor in times of trouble, or the “weak link”.